Undergraduate Programs
The School of Economics (SE) offers two undergraduate programs, namely Bachelor of Science in 12 Economics (BSE) and Bachelor of Science in Business Economics (BSBE), that have different 13 curricula but share common courses. Several courses are required in both programs, while other courses 14 are required in the BSBE and can be taken as Econ elective in the BSE.
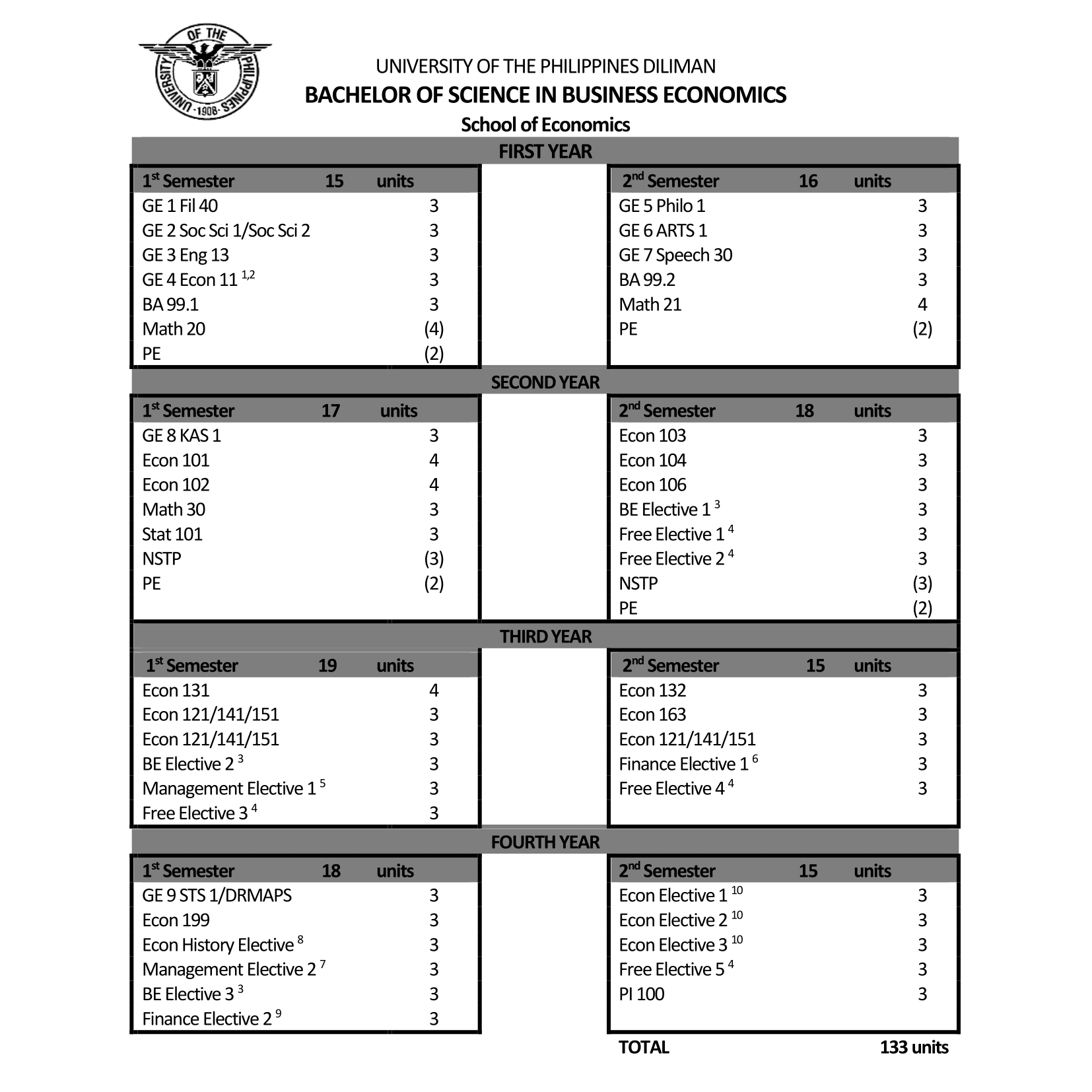
Bachelor of Science in Business Economics
Click below to download the Curriculum Checklist under the BS Business Economics degree program, as approved by BOR on February 25, 2025:

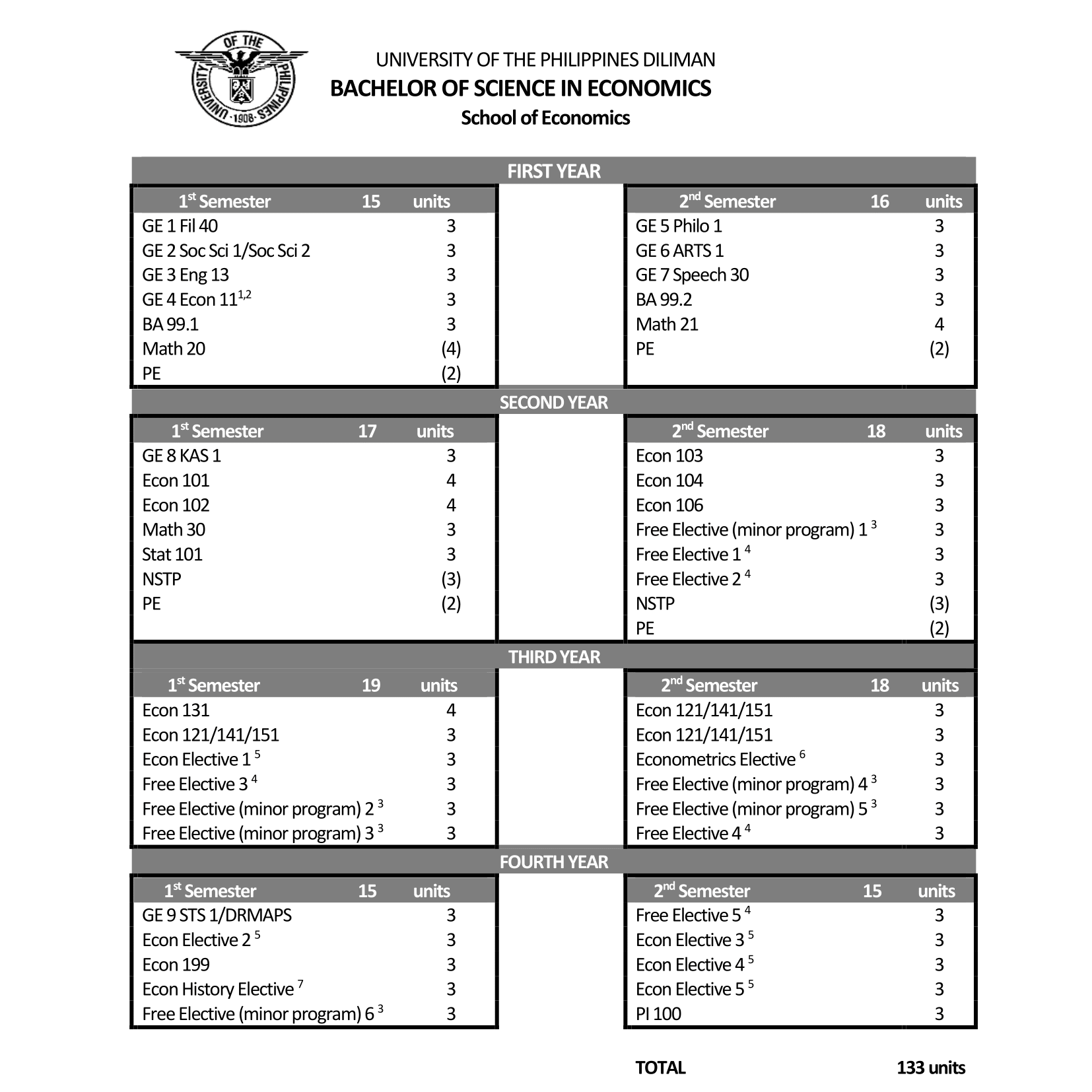
Bachelor of Science in Economics
Click below to download the Curriculum Checklist under the BS Economics degree program, as approved by BOR on February 25, 2025:

Bachelor of Science in Economics Minor Programs
MINOR PROGRAM OPTIONS
OPTION 1: Minor Programs Taken Outside of the School
Students enrolled in the BS Economics program may apply for minor programs offered by other colleges or institutes within the university. These include the following:
- College of Education: Minor in Professional Education (18 units)
- Institute of Mathematics: Minor in Mathematical Foundations and Methods (20 units)
- Other possible minor programs include: Political Science, International Studies, Public Administration, History, Psychology, Sociology, Philosophy, or Urban and Resource Planning, among others.
OPTION 2: Default, Non-Minor Track
Students who do not pursue or are not accepted into a Minor Program will follow the default, non-minor track under the School of Economics.
MINOR PROGRAM ADMISSION
To qualify for a Minor Program, a student must:
- Have completed at least two (2) semesters of residency.
- Be in good academic standing.
- Secure an endorsement from the School of Economics. A student will be given one (1) endorsement for a Minor Program throughout the duration of their Bachelor’s degree.
- Be accepted by the unit offering the Minor Program. This unit may impose additional requirements, which can be found on the website of the offering unit.
RETENTION RULES
To be retained in a Minor Program, the student must remain in good academic standing. In addition, the Minor-offering unit may impose other retention requirements.
Students who are not retained in their Minor Program shall be deemed to follow the Non-Minor option.
MINOR PROGRAM APPLICATION PROCESS
- Student submits the endorsement form to SE101. The School Records Evaluator (SRE) will verify the information in the form.
- The SRE will forward the form to the Director of Undergraduate Studies for the first endorsement.
- The Director for Undergraduate Studies will forward the form to the College Secretary for final endorsement.
- The College Secretary will return the form to the SRE.
- The SRE will release the signed form to the student.
- The student will retrieve the signed form from SE101.
Note:The School of Economics (UPSE) only endorses applications. It is the responsibility of the student to ensure that they are accepted by the Minor-offering college or unit. Only accepted minors will be credited upon graduation.
Minor in Professional Education
Website: https://educ.upd.edu.ph/minor-in-professional-education-mpe/
Students will be assessed after taking nine (9) units of the prescribed courses. A GWA of 2.5 or better in these courses is required for retention in the program.
The College of Education offers an 18-unit Minor in Professional Education (MPE) program that allows non-Education undergraduate students to pursue teaching careers. The MPE is designed to prepare students to teach in secondary and senior high schools, in accordance with Republic Act 9293, which permits non-Education degree holders to take the Licensure Examination for Teachers (LET), provided they complete 18 units of Professional Education courses.

(Source: Minor in Professional Education, University of the Philippines College of Education website, accessed 20 February 2025)
Minor in Mathematical Foundations and Methods
Website: https://math.upd.edu.ph/programs/minor-in-mathematical-foundations-and-methods
The Minor in Mathematical Foundations and Methods program is an undergraduate minor program that consists of mathematics courses aimed at preparing non-B.S. Mathematics students for advanced studies in quantitative-oriented fields. It is designed to provide students with a strong foundation in statistics, calculus, and discrete mathematics. Additionally, the program seeks to develop students’ capacity for abstract reasoning, familiarity with mathematical proofs, and computational skills.
The program aims to train students who can:
- Use mathematical tools and techniques in framing problems in the physical, life, and social sciences;
- Determine the validity of an argument using mathematical reasoning; and
- Apply mathematical knowledge and computational skills to concrete problems in the physical, life, and social sciences.
The following are required for admission to the minor program:
- Completion of Math 22 and Stat 101, or their equivalents, and at least two semesters of residency;
- Good academic standing with a Cumulative Weighted Average (CWA) of 2.5 or better;
- Endorsement by the College Secretary of the Home Unit; and
- Acceptance by the College Secretary of the College of Science.
To remain in the program, the student must:
- Remain in good academic standing with a GWA of 2.5 or better.
- Not incur a second failing grade (includes 4.0, 5.0, DRP with “failing” remark, and DRP unofficial) in Math 23, Math 40, and Math 108.
- Not incur a third failing grade (includes 4.0, 5.0, DRP with “failing” remark, and DRP unofficial) in Math 122, Math 150.1, Math 123.1, Math 133, Math 158, Math 162, and Math 180.1.
- Follow the Program of Study advised by the Home Unit.
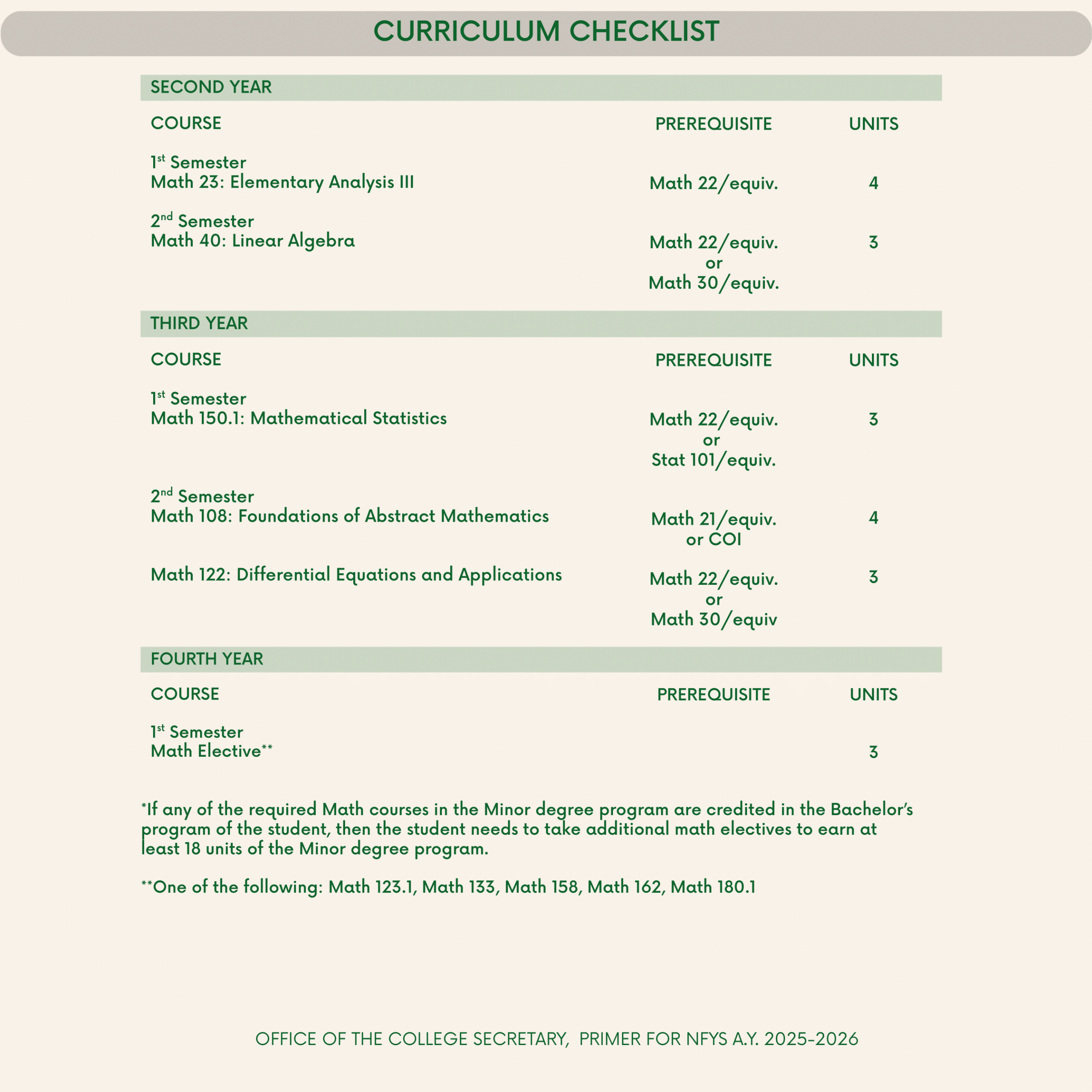
(Source: Minor in Mathematical Foundations and Methods, Programs, UP Institute of Mathematics website, accessed 20 February 2025)
Individual Course Descriptions
GE COURSE
- Econ 11 (Markets and the State). Essential economic concepts and their use in analyzing real-world issues.
UNDERGRADUATE
- BA 99.1 (Fundamental Accounting Theory and Practice I).
- BA 99.2 (Fundamental Accounting Theory and Practice II).
Prereq: BA 99.1
- CWTS 1 & 2. For Econ majors only.
Prereq: Sophomore standing
- Econ 100.1 (Introduction to Macroeconomic Theory and Policy). Basic concepts in macroeconomics and their applications.
Prereq: None
- Econ 100.2 (Introduction to Microeconomic Theory and Policy). Basic concepts in microeconomics and their applications.
Prereq: None
- Econ 101 (Macroeconomics I). National income accounting; consumption and investment decisions; income and employment determination; monetary and fiscal policies; growth.
Prereq: Econ 11/COI, Math 21/COI
- Econ 102 (Microeconomics I). Demand and supply; consumer theory; producer theory; price determination in competitive markets and partial equilibrium; imperfect competition; externalities and public goods.
Prereq: Econ 11/COI, Math 21/COI
- Econ 103 (Macroeconomics II). Open economy models; global financial system and crises, intertemporal macroeconomics.
Prereq: Econ 101/COI
- Econ 104 (Microeconomics II). Social choice; choice under risk and uncertainty; auctions; asymmetric information; contracts; general equilibrium and welfare.
Prereq: Econ 102/COI
- Econ 106 (Elements of Mathematical Economics). Mathematical approaches to elementary economic theory.
Prereq: Econ 101/COI, Econ 102/COI, Math 30/COI
- Econ 109 (History of Economic Thought). Evolution of basic economic ideas and their social and intellectual context.
Prereq: Econ 101/COI, Econ 102/COI
- Econ 111 (General Economic History). Economic change and the evolution of economic institutions in selected countries.
Prereq: Econ 101/COI, Econ 102/COI
- Econ 118 (Special Topics in Economic History). May be taken two times provided the topics are different.
Prereq: Econ 101/COI, Econ 102/COI
- Econ 121 (Money and Banking). Nature and role of money; banks and other financial intermediaries; central banking and banking regulations; open economy issues; efficient-markets theory; development finance. Prereq: Econ 101/COI, Econ 102/COI
- Econ 122 (Financial Economics I). Asset markets and asset pricing; decision-making under uncertainty; portfolio selection; capital asset pricing model.
Prereq: Econ 121/COI
- Econ 123 (Financial Economics II). Security analysis and portfolio management; arbitrage; futures, options and other derivatives; behavioural finance.
Prereq: Econ 122/COI
- Econ 131 (Quantitative Economics). Representation of economic phenomena in terms of elementary mathematical and statistical models.
Prereq: Econ 101/COI, Econ 102/COI, Math 21/COI, Stat 101/COI.
- Econ 132 (Business Forecasting). Regression analysis with time series data; ARIMA models; simultaneous-equation model forecasting; methods of microeconomic forecasting.
Prereq: Econ 131/COI
- Econ 138 (Special Topics in Econometrics). May be taken two times provided the topics are different.
Prereq: Econ 131/COI
- Econ 141 (International Economics). International trade and finance; commercial policy and the macroeconomics of an open economy.
Prereq: Econ 101/COI, Econ 102/COI
- Econ 151 (Public Economics). Market failure; collective choice; theory of government expenditures and taxation.
Prereq: Econ 101/COI, Econ 102/COI
- Econ 153 (Project Evaluation). Discounted cash-flow analysis; social opportunity cost pricing; applications to public-sector projects with case studies; post-evaluation techniques.
Prereq: Econ 101/COI, Econ 102/COI
- Econ 161 (Industrial Organization). Analysis of firms and markets; pricing, product, and investment decisions in theory and in practice; policies on competition and on protection; business and its environment.
Prereq: Econ 101/COI, Econ 102/COI
- Econ 162 (Managerial Economics). Theory of the firm; demand theory and estimation; production and cost theory and estimation; analysis of strategic business practices.
Prereq: Econ 102/COI
- Econ 163 (The Law and Economics of Business Transactions). Introduction to law and legal institutions; economic approach to law; Philippine laws on obligations and contract; economics of valid contract and remedies for contract breach.
Prereq: Econ 102/COI
- Econ 167 (Economics of Marketing and Management). This course applies economic principles of marketing towards creating effective marketing strategies in the areas of product development/design,product pricing, distribution and promotion of goods and services.
Prereq: Econ 102/COI
- Econ 168 (Special Topics in Law and Economics). May be taken two times provided the topics are different.
Prereq: Econ 101/COI, Econ 102/COI
- Econ 171 (Economics of Agriculture). Agriculture in strategies for economic development; economics of rural institutions; analysis of agricultural policy.
Prereq: Econ 101/COI, Econ 102/COI
- Econ 172 (Resource and Environmental Economics). Introduction to the analysis of problems and management of natural resources; environmental problems and policies.
Prereq: Econ 101/COI, Econ 102/COI
- Econ 178 (Special Topics in Resource and Environmental Economics). May be taken two times provided the topics are different.
Prereq: Econ 172/COI
- Econ 181 (Labor Economics). Determinants of wage levels and wage structure; employment; nonwage aspects of employment; aspects of human capital theory.
Prereq: Econ 101/COI, Econ 102/COI
- Econ 186 (Health Economics). Demand for and supply of health care; role of government in health care; organization and financing of health care services; problems associated with delivery system.
Prereq: Econ 101/COI, Econ 102/COI
- Econ 190.1 (International Trade, Payments, and Development Policy). Basic concepts and issues in foreign trade and external payments affecting developing countries; analysis of policies and their effects.
Prereq: Econ 100.1 and 100.2/COI; or Econ 101 and 102/COI
- Econ 190.2 (Monetary, Fiscal and Development Policy). Basic concepts and issues in money, credit, taxation, and public spending in the context of development; analysis of policies and their effects.
Prereq: Econ 100.1 and 100.2/COI; or Econ 101 and 102/COI
- Econ 191 (Development Economics). Theories and problems of economic development; survey of the development experience in low and high-income countries.
Prereq: Econ 101/COI, Econ 102/COI
- Econ 195 (Reading Course in Economics). Individual work on special topics not included in the announces course offerings.
Prereq: Econ 101/COI, Econ 102/COI
- Econ 196 (Urban and Regional Economics). Introduction to location theory; the urban economy; regional income theory; regional interdependence.
Prereq: Econ 101/COI, Econ 102/COI
- Econ 198 (Special Topics in Economics). May be taken 2 or more times provided the topics are different.
Prereq: Econ 101/COI, Econ 102/COI
- Econ 199 (Seminar).
Prereq: Senior Standing, Econ 131/COI
Rules on Academic Standing
A. University Rules on Academic Standing
“A student is in good scholastic standing if at the end of the semester s/he obtains a final grade of ‘3’ or higher in at least 75% of the total number of academic units in which s/he is registered. However, colleges may impose additional rules on ‘good scholastic standing’ such as a minimum grade average or required number of units passed per semester/year.”
(UP Diliman General Catalogue, 2014)
B. UPSE Rules on Academic Standing
- At the end of the Junior year or the midyear term of it, a student must have:
- a cumulative weighted average grade (WAG) of 2.50 or better in all grades received in courses credited in the curriculum; and
- a cumulative economics weighted average (EWA) of 2.50 or better. [a]
- Otherwise, the student is dismissed from the School.
- At the end of every semester or midyear term, a student must obtain:
- a cumulative WAG of 2.50 or better in all grades received in courses credited in the curriculum;
- a cumulative EWA of 2.50 or better; [a] and
- regular grades (i.e., excluding INCs and DRPs) in at least 60% of the units registered as of the last day of registration.
- Otherwise, the student will be placed on probation the following term. Probation may be removed by satisfying requirements (2a), (2b), and (2c) at the end of the semester or midyear term the student was on probation.
- Any student on probation who fails to satisfy requirements (2a), (2b), and (2c) at the end of the semester or midyear term the student was on probation will be dismissed from the School.
- A student must pass Econ 106 and Econ 131 within four (4) semesters from first enrolling in either Econ 101 or Econ 102, inclusive of the semester of first enrollment in either subject; otherwise, the student will be put under probation. Failure to satisfy this rule at the end of the semester or midyear term the student was put on probation will result in dismissal from the School.
- A cumulative WAG of 2.50 or better and a cumulative EWA of 2.50 or better are required for graduation.
[a] For purposes of determining scholastic standing, the EWA is calculated using the following inclusion and exclusion criteria:
- Inclusions: All undergraduate Econ courses taken in UPSE, whether credited as major subjects, Econ electives, or free electives; validated 4-unit Econ 101 and 4-unit Econ 102 taken outside UPSE.
- Exclusion: Econ 11, Econ 100.1, Econ 100.2, Econ 190.1, and Econ 190.2; other Econ subjects taken outside UPSE.
Admissions
(Updated: 21 May 2024)
A. Regular Admission
Freshman students are admitted directly to the School through the U.P. College Admissions Test.
B. Admission for Shifting/Transferring to UPSE
I. General guidelines
- Admission is subject to the quota conditions of UPSE.
- UPSE only accepts shiftees and transferees at the beginning of the academic year.
- Applications for shifting/transfer must be submitted online not later than 30 calendar days after the end of classes of the second semester of the preceding academic year. Please refer to UP Diliman’s official academic calendar.
- Computation of the general weighted average (GWA) and curriculum weighted average (CWA) will be based on the applicant’s numerical grades (or their equivalent if taken outside the UP System). Applicants who previously received non-numerical grades (e.g., Pass or Fail) in any of their subjects (especially during the pandemic) are required to submit the numerical equivalent.
- Successful applicants must apply for the crediting of previously taken courses within the first semester of their admission to UPSE.
II. Documentary Requirements
APPLY ONLINE↖️
- Recent ID picture in JPEG or PNG format.
- Transcript of Records (TOR) or True Copy of Grades (TCG) for courses taken from first year to the most recent semester, duly certified by the College Secretary or Registrar.
- If you previously received non-numerical grades in any of your subjects, proof of their conversion to numerical equivalent (e.g., letter from instructor, certification from Department or Registrar).
- For non-UP students, proof that you have taken a course similar to Math 21 (e.g., syllabus of the Math course taken, certification from your school’s Math Department or Registrar). Click here for the topics covered in Math 21: https://math.upd.edu.ph/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/math-21.pdf.
- Completely filled out curriculum checklist.
- For BS Econ applicants: https://econ.upd.edu.ph/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/CC-BSE_as.xlsx
- For BS BE applicants: https://econ.upd.edu.ph/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/CC-BSBE_as.xlsx
- For UP students, certification issued by the current College that you are not under contract to finish your degree program in the said College.
- Certificate of good moral character.
III. Minimum Requirements by Category
- Shiftees within UPSE
- Good scholastic standing (i.e., not on probation).
- Not of senior standing at the time of application.
- For current BS Econ students shifting to BS BE: must have more than 30 units remaining in the BS Econ curriculum.
- For current BS BE students shifting to BS Econ: must have more than 33 units remaining in the BS BE curriculum.
- Shiftees within UP Diliman (excluding UPSE) and Transferees from other UP units
- Completed at least 30 academic units.
- General weighted average (GWA) of 2.25 or better AND curriculum weighted average (CWA) of 2.25 or better. GWA is calculated based on grades in all courses taken by the student. CWA is based only on the student’s grades in courses that will be credited in the target program (i.e., BS Econ or BS BE).
- Grade of 2.5 or better in Math 21 (or its equivalent) OR average grade of 2.5 or better in Math 21 and Math 30 (or their equivalent) if the applicant has taken both Math subjects (or their equivalent). Applicants who have not taken Math 21 (or its equivalent) at the time of application may be considered provided that: a) they take Math 21 (or its equivalent) during the application period (i.e., midyear term); and b) they earn a grade of 2.5 or better in Math 21 (or its equivalent). See https://econ.upd.edu.ph/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/MATH-21-SUBSTITUTION-GUIDE.pdf for the list of courses equivalent to Math 21.
- Not of senior standing at the time of application.
- Applicants to BS Econ must have more than 30 units remaining in the BS Econ curriculum.
- Applicants to BS BE must have more than 33 units remaining in the BS BE curriculum.
- Transferees from other Schools/Universities
- Completed at least 33 academic units in current school/university.
- General weighted average (GWA) of 1.5 or better. GWA is calculated based on grades in all courses taken by the student.
- Average grade of 1.5 or better in all math subjects taken.
- Grade of 1.5 or better in a course similar to UP Diliman’s Math 21 (Elementary Analysis I). Click here for the topics covered in Math 21: https://math.upd.edu.ph/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/math-21.pdf. Applicants must submit a proof that they have taken a course similar to Math 21 (e.g., syllabus of the Math course taken, certification from the school’s Math Department or Registrar).
- Applicants who belong to this category must submit their applications to the Office of the University Registrar (OUR). Click here for details: https://upd.edu.ph/transfer-admission/. However, you are encouraged to also fill out the UPSE Shifting/Transfer Application Form.
Inquiries may be directed to:
Office of the College Secretary
School of Economics, University of the Philippines
Quezon City, Philippines 1101
Tel. (632) 9205482 and 9818500 local 3477
c/o Ms. Joyce M. Evangelista
Fax (632) 9205482 and 9818500 local 3477
E-mail: upse101.upd@up.edu.ph
PROGRAM OVERVIEW
The UP School of Economics offers courses leading to the degrees of Doctor of Philosophy (Economics), Master of Arts (Economics), and Master in Development Economics (MDE). These programs are designed to provide future economists in academe, government, industry, non-governmental and international organizations with rigorous training in the methods and applications of economic analysis.
Currently, there are three programs offered for graduate studies::
- Master of Arts in Economics (MA)
- Master in development Economics (MDE)
- Doctor of Philosophy in Economics (PhD)
These programs are designed to provide future economists in academe, government, industry, non-government, and international organizations with rigorous training in the methods and applications of economic analysis.
Admission to these programs is not limited to undergraduate degree holders in economics. Those with undergraduate degrees in mathematics, statistics, engineering, physical sciences, agricultural sciences, and other social science are likewise encouraged to apply.
Doctor of Philosophy in Economics Degree Requirements
In order to qualify for the Ph.D. degree, a student must successfully complete 48 units of formal coursework, pass a comprehensive examination with a grade that advances him or her to candidacy, and write a dissertation. Completion of all requirements for the Ph.D. degree would normally take three years of full-time study.
Course Requirements
The School requires all its doctoral students to be proficient in economic theory and have some training in quantitative methods as well as familiarity with economic history. Grades of 2.0 or better are required for every course outlined:
| CATEGORY | SUBJECT |
| Economic Theory (required) |
|
| Mathematics |
|
| Statistics and Econometrics |
|
| Economic History or the History of Economic Thought |
|
Grade Requirements
Under University rules, a student must maintain a cumulative weighted grade average of 1.75 at the end of each academic year to remain in good standing. Failure to satisfy this grade requirement will result in the student’s disqualification from the program. To successfully complete the program, a grade of 2.5 or better must be earned in each course towards an overall weighted average of 1.75 or better.
Program of Study
Admission to the Ph.D. program presupposes completion of at least 24 units (two semesters) of coursework under the master’s program. The doctoral program requires the student to pass a comprehensive examination given after the second semester of second-year coursework.
MASTER OF ARTS IN ECONOMICS
To qualify for the M.A. (Econ) degree, a student must successfully complete a program of studies approved by the Department. A student may choose from either of two tracks:
- The thesis track consists of 24 units of formal coursework, a master’s qualifying examination, and a master’s thesis of six (6) units. Acceptance of the thesis is based on the recommendation of the adviser and the endorsement of the reader.
- The non-thesis track consists of 30 units of coursework, a master’s qualifying and comprehensive examinations, and a research seminar course (Economics 299) in which a paper is required.
These requirements are normally completed in three semesters of full-time study. In the first year, the student is required to complete 24 units of formal coursework at the 200 level, including Macroeconomic Theory I and II, Microeconomic Theory I and II, Economic Statistics, and Econometrics I.
The Master’s qualifying examination which is given at the end of the second semester consists of a four-hour test in economic theory and another two-hour test in quantitative methods.
Completion of at least 24 units of coursework is a requirement for taking the examination. Students who fail the examination may retake it only once.
In addition to the Master’s qualifying examination, non-thesis track students will take a Master’s comprehensive examination on a chosen field in Economics. It may be taken by a student only after completing the course work and obtaining a cumulative weighted average of 2.0 or better.
Grade Requirements
University rules require a student to maintain a cumulative weighted average of 2.0 in each academic year to remain in good standing.
To successfully complete the program, a student should earn a grade of 2.5 (equivalent to satisfactory) or better in each course, and a weighted average of 2.0 or better for the courses contained in the study program.
Program of Study
| FIRST SEMESTER | SECOND SEMESTER | THIRD SEMESTER |
|
|
Thesis track:
Master’s thesis (Econ 300) |
|
|
Non-thesis track:
Research Seminar I (Econ 299) Elective* Elective* M.A.Comprehensive Examination |
|
|
|
|
Master’s qualifying examination |
**Electives are available in the following fields: Agricultural Economics, Demographic Economics, Health Economics, Human Resource Economics, International Economics, Monetary Economics, Public Economics, and Industrial Economics.
MASTER IN DEVELOPMENT ECONOMICS
To qualify for the MDE degree, a student must successfully complete a program of study approved by the Department. A student may choose from either of two tracks:
- The thesis track consists of 24 units of formal coursework and a master’s thesis of 6 units. Acceptance of the thesis is based on the recommendation of the adviser and the endorsement of the reader.
- The non-thesis track consists of 30 units of formal coursework, a research seminar course (Econ 299) in which a paper is required, and passing the MDE comprehensive examination.
These requirements are normally completed in three semesters of full-time study. The comprehensive examination shall consist of a four-hour examination in economic analysis (macroeconomics and microeconomics) and another two-hour examination in the field of economic development. It can only be taken after the student has completed all course requirements. The examination is passed or failed as a whole, with a passing mark equivalent to a grade of 2.0. Students who fail the examination may retake it only once.
Grade Requirements
A cumulative weighted average of 2.0 or better must be maintained at the end of every academic year for a student to remain in good standing. Failure to meet this requirement for two academic years will disqualify the student from the program. In addition, a student should earn a grade of 2.5 or better in each course. To qualify for graduation, a student must obtain a general weighted average of 2.0 or better.
Program of Study
| FIRST SEMESTER | SECOND SEMESTER | THIRD SEMESTER |
|
|
Thesis track:
Master’s thesis (Econ 300) |
|
|
Non-thesis track:
Research Seminar I (Econ 299) Take any two of the following courses:
MDE Comprehensive Examination |
|
|
|
|
|
ADMISSIONS
UP School of Economics is now accepting applications, scan the QR code to apply!

REQUIRED DOCUMENTS
Applications to the U.P. School of Economics Graduate programs may be submitted through the Student Applications and Admissions System (SAAS). An applicant shall create an account to the website, and upload the original copy of the following documents:
- Transcript of Records on the courses taken by the applicant at the undergraduate and graduate level
- Statement of purpose
- Diploma or equivalent document certifying that the applicant has completed a Bachelor’s degree
- 2×2 picture (head-shot)
- TOEFL/IELTS Certification/Statement of English Mastery (for foreign applicants)
- Payment receipt for application fee of PhP1,000 (or US$40 for foreign applicants)
An applicant must deposit the amount to the following bank details:
Bank of Philippine Islands (Loyola Branch)
Current Account # 3081-0755-13
Account Name: UPSE Fellowships
Bank Routing Code: BOPIPHMM (Swift Code)
Shortlisted applicants shall be required to take the entrance examinations usually scheduled in April prior to the start of the academic year in August. Alternatively, they may submit their GRE or GMAT scores obtained within the last two years. The interview for the shortlisted applicants is scheduled a few days after the test.
Qualified applicants will be given probational admissions and invited to attend the four to five (4-5) weeks face-to-face classes between 8AM-5PM.
Below is the admission process for the UPSE graduate programs:

GRADUATE COURSES
Click here for the complete list of SE Courses.
Economics (Econ)
201 Macroeconomic Theory I. Theories of income and employment determination and the business cycle; theories of inflation and unemployment; the macroeconomy and the fiscal, monetary, and external sectors; open economy macroeconomics; stabilization policies. 3 u.
202 Microeconomic Theory I. Preference and choice; consumer choice and demand; production, costs, profits and supply; competitive markets; market structure; externalities, public goods, and market failure; general equilibrium and welfare. 3 u.
203 Macroeconomic Theory II. Theories of consumption, saving, and investment; theories of growth; theories of economic development and accumulation. Prereq: Econ 201/COI. 3 u.
204 Microeconomic Theory II. Information asymmetry; hidden action; equilibrium under uncertainty and over time; social choice; axiomatic bargaining; incentive- and mechanism design. Prereq: Econ 202/COI. 3 u.
205a Special Topics in Economic Theory. 3 u.
206a Mathematical Economics. Applications of linear algebra, theory of functions, and linear and nonlinear optimization in economic theory. 3 u.
207a Special Topics in Mathematical Economics. 3 u.
209a History of Economic Thought. The development of important theoretical concepts in economics and political economy; a critical reading of the original sources. 3 u.
211a Economic History. Economic change, development, and the evolution of important institutions in selected countries; the application of economic analysis to historical issues. 3 u.
221a Monetary Economics. Classical monetary theory; Keynesian models; rational expectations models; development finance; monetary policy. 3 u.
222a Advanced Monetary Economics. 3 u.
223a Special Topics in Monetary Economics. 3 u.
231 Economic Statistics. Statistical methods in the analysis of economic data meeting minimum needs for quantitative research work in economics. Prereq: COI. 3 u.
232 Econometrics I. Estimation of a single linear relationship; the simultaneous equations approach. Prereq: Econ 201, 202, 231/COI. 3 u.
233 Econometrics II. Simultaneous equations systems, estimation methods and problems. Prereq: Econ 201, 202, 232/COI. 3 u.
236a Economic-Demographic Methods. Issues and problems in demographic measurement; sources and quality of demographic data; applications of demographic concepts; model estimation. 3 u.
241a International Economics. Theory of international trade and factor movements; theory of protection and domestic distortions, exchange-rate theories and balance of payments adjustment mechanisms; macroeconomic policy in an open economy. 3 u.
242a Advanced International Economics. 3 u.
243a Special Topics in International Economics. 3 u.
251a Public Economics. Market failures; theory of public goods; public choice and incentive mechanisms for goods allocation; public sector pricing; incentive effects of taxation; optimal taxation and redistribution. 3 u.
252* Advanced Public Economics. 3 u.
253* Special Topics in Public Economics. 3 u.
261 Industrial Economics. Analysis of market structure, conduct and performance; determinants of the behavior, scale, scope and organization of business firms; public policy towards business. Prereq: Econ 202/COI. 3 u.
271a Economics of Agriculture. Theoretical and empirical analyses of rural institutions and agricultural resource use; technological change; and macro-aspects of agriculture. 3 u.
272a Special Topics in Agricultural Economics. 3 u.
275a Natural Resource and Environmental Economics. Analysis of problems in the development and management of exhaustible and renewable resources; environmental problems and policies. 3 u.
276a Special Topics in Natural Resource and Environmental Economics. 3 u.
281a Human Resource Economics. Theories of labor supply and demand; aspects of human capital theory; wage structure; labor markets in developing countries; models of unemployment. 3 u.
282a Special Topics in Human Resource Economics. 3 u.
283a Economics of Population. Determinants of mortality, fertility and migration; interaction between population growth and development; aging; population policy and development planning. 3 u.
284a Special Topics in the Economics of Population. 3 u.
286a Health Economics. Approaches to the study of health economics; determinants of health; behavior of health care markets; non-market alternatives to health care provisions; applications to health problems in developing countries. 3u.
287a Special Topics in Health Economics. 3 u.
291* Development Economics I. Theories of economic growth and development; background and comparative analyses of growth in developed and developing countries.
292a Development Economics II. Long-term strategies and policies for economic growth and their underlying problems and issues; projections from macroeconomic models; project evaluation. 3 u.
293a Special Topics in Development Economics. 3 u.
295a Reading Course in Graduate Economics. 3 u.
296a Urban and Regional Economics. City structure and city systems; urban growth models; location theory; regional income theory and regional interdependence. 3 u.
298a Special Studies in Economics. 3 u.; may be taken more than once provided topics are different.
299a Research Seminar I. 3 u.
300a Master’s Thesis. 6 u.
301a Advanced Macroeconomic Theory. 3 u.
302a Advanced Microeconomic Theory. 3 u.
399a Research Seminar II. 3 u.
400a Dissertation. 24 u
Development Economics (DE)
201 Economic Analysis I. The measurement, analysis, and control of aggregate economic activity; money and the price level; the role of government; models of the open economy; international trade and the balance of payments. 3 u.
202 Economic Analysis II. The theory of consumer behavior and the theory of the firm; pricing and allocation of goods and factors of production in different market situations; economic efficiency and welfare considerations. 3 u.
206 Quantitative Methods I. Mathematical tools for economic analysis and model building; applications to macroeconomic and microeconomic problems; optimization techniques. 3 u.
231 Quantitative Methods II. The analysis of economic data; sample survey techniques; statistical tools for model estimation and forecasting; computer applications. 3 u.
241b Trade Policy and Development. Theories of trade, trade protection, regionalism and materialism; relationship between trade and development; global trade governance; special issues affecting global trade. 3 u.
251 Public Sector Economics for Development. Taxation, resource allocation, and welfare; public expenditures and collective consumption; efficiency and equity aspects of fiscal policy. 3 u.
252c Local Public Economics. Economic analysis of local or subnational governments and their roles in and contributions to economic development; public financial management and expenditure analysis; local government performance and innovations. 3 u.
253 Project Analysis and Evaluation. Methods of project appraisal, selection, and post-evaluation from the private and social viewpoints; case studies of selected Philippine projects. 3 u.
291 Growth, Poverty and Institutions. Economic development problems and analytical models of growth and development; structural adjustment; poverty and income distribution. 3 u.
292 Program Evaluation Issues and experiences in economic development; techniques in program evaluation. 3 u.
293b Institutional and Policy Analysis. Political economy of policy making; impact of political institutions, power relations and social dynamics on the efficiency and effectiveness of public policies. 3 u.
298b Special Problems in Development Economics. 3 u.
aPrereq: Econ 201, 202/COI
bPrereq: DE 201, 202/COI
Guidelines for Recognition as UP School of Economics-Based Organization
UPSE Awards and Recognition is acknowledgments given to students who demonstrate excellence, leadership, or significant contributions in various aspects of school life. These honors are designed not just to celebrate achievements, but to motivate students to strive for personal growth, academic success, and social responsibility. These awards can be academic, recognizing outstanding performance in specific subjects or overall academic progress, or they can highlight positive character traits, leadership skills, or participation in extracurricular activities.
Gawad Jose Encarnacion para sa Kagalingan sa Ekonomiks, o Jose Encarnacion Award for Excellence in Economics.
Ang parangal na ito ay tradisyunal na ipinagkakaloob sa mag-aaral na undergraduate na nagkamít ng pínakamataas na Economics Weighted Average.
Si Jose Enarnacion, Jr. ay isa sa mga pinakadakílang guro at mananaliksik ng ekonomiks sa Pilipinas. Siya ang pinakamatagal na dekano ng School of Ekonomics. Nagsilbi siya sa katungkulang ito ng dalawampung (20) taon. Ipinanganak noong 1928 at namatay noong 1998, si Dekano Encarnacion din ang kauna-unahang Pambansang Siyentipiko (National Scientist) para sa Ekonomiks. Bukod sa pagiging tagapagbunsod ng edukasyong ekonomiks sa Pilipinas, si Dekano Encarnacion din ang pangunahing nagsulong ng teorya ng lexicographic preferences.
Taun-taon, ipinagkakaloob ang Gawad para sa Kagalingan sa Ekonomiks sa ngalan ni Dekano Encarnacion bilang pagkilala sa kaniyang mga ambag sa paaralan at sa larangan ng ekonomiks.





